Residential solar panel system
Residential solar panel systems are a type of renewable energy system that generates electricity from the sun’s energy. The system is made up of several components, including solar panels, an inverter, a mounting and racking system, and a monitoring system. Some systems may also include batteries to store excess energy for later use. Residential solar panel systems offer numerous benefits, including a reduction in energy costs, an increase in home value, and environmental benefits. They also provide homeowners with greater energy independence and the ability to generate their own electricity.
This blog post will provide an overview of residential solar panel systems, including the components of the system, the types of systems available, factors to consider when choosing a system, the installation process, and maintenance and upkeep. Additionally, it will explore the benefits and potential drawbacks of residential solar panel systems, and offer a conclusion on the importance and future of this technology.
Components of a residential solar panel system
Solar panels
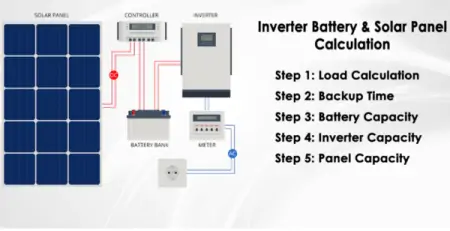
Solar panels are the primary component of a residential solar panel system. They are made up of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter
The inverter is another essential component of a residential solar panel system. It converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power homes and appliances.
Racking and mounting system
The racking and mounting system is used to securely attach the solar panels to the roof of a home or a ground-mounted system. The mounting system must be strong enough to support the weight of the panels and withstand harsh weather conditions.
Monitoring system
A monitoring system allows homeowners to track the performance of their solar panel system. It can provide information on energy production, energy usage, and any potential issues with the system.
Batteries (optional)
Batteries are an optional component of a residential solar panel system. They allow homeowners to store excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use when energy demand is higher or when there is no sunlight available. Batteries can also provide backup power in the event of a power outage.
Types of residential solar panel systems
Grid-tied system
A grid-tied system is the most common type of residential solar panel system. It is connected to the electrical grid and allows homeowners to use both solar-generated electricity and electricity from the grid. Excess energy generated by the solar panels can be sold back to the utility company for credit on the homeowner’s electricity bill.
Off-grid system
An off-grid system is a self-sufficient solar panel system that is not connected to the electrical grid. These systems typically require batteries to store excess energy for later use when the sun is not shining. Off-grid systems are most commonly used in remote areas where there is no access to the grid.
Hybrid system
A hybrid system is a combination of a grid-tied and off-grid system. It allows homeowners to use both solar-generated electricity and electricity from the grid, while also having a battery backup system for use during power outages or when energy demand is higher than solar production. Hybrid systems can offer the best of both worlds by providing energy independence while still being connected to the grid.
Factors to consider when choosing a residential solar panel system
Energy needs
The first factor to consider when choosing a residential solar panel system is your energy needs. You’ll want to determine how much energy you use on average and how much of that energy you want to generate with your solar panel system. This will help you determine how many solar panels you need and what size system is best for your home.
Budget
Another important factor to consider is your budget. Solar panel systems can range in price depending on the size of the system, the type of panels used, and installation costs. You’ll want to determine how much you’re willing to spend and whether you’ll be financing the system or paying for it upfront.
Roof size and orientation
The size and orientation of your roof will also play a role in choosing a residential solar panel system. You’ll want to determine whether your roof is large enough to accommodate the number of panels you need and whether it has a favorable orientation for maximum sun exposure.
Climate and weather conditions
Your climate and weather conditions will also play a role in choosing a solar panel system. For example, if you live in an area with a lot of cloudy or rainy days, you may need a larger system to generate enough energy to power your home.
Local regulations and incentives
Finally, you’ll want to consider local regulations and incentives when choosing a solar panel system. Some areas may have regulations that impact the type of system you can install, while others may offer incentives such as tax credits or rebates to help offset the cost of the system.
The installation process for residential solar panel systems
Site assessment and system design
The first step in the installation process is a site assessment and system design. This involves a solar professional visiting your home to assess your roof, determine the best location for the panels, and design a system that meets your energy needs and fits your budget.
Permitting and paperwork
Once the system design is complete, you’ll need to obtain the necessary permits and paperwork to move forward with the installation. This may include building permits, electrical permits, and approval from your local utility company.
Installation and connection to the grid
Once the permits and paperwork are in order, the solar panels will be installed on your roof or on a ground-mounted system. This process typically takes one to three days depending on the size of the system. After installation, the system will be connected to the grid through an inverter, which converts the energy generated by the panels into usable electricity for your home.
Inspection and approval
After the installation and connection to the grid is complete, a final inspection will be performed to ensure the system is up to code and meets safety requirements. Once the system is approved, you’ll be able to start generating your own clean energy and reducing your dependence on the grid.
Maintenance and upkeep of residential solar panel systems
Cleaning and maintenance of solar panels
Regular cleaning and maintenance of solar panels is important to ensure they operate at maximum efficiency. This involves removing debris, dirt, and other contaminants that can accumulate on the panels over time. You can clean the panels yourself using a soft brush and water, or hire a professional cleaning service to do it for you.
Monitoring system performance
To ensure your solar panel system is operating at optimal levels, it’s important to regularly monitor its performance. This can be done using a monitoring system that tracks the amount of energy being produced by the panels and identifies any issues that may arise.
Upgrading and replacing components
Over time, components of your solar panel system may need to be upgraded or replaced. This could include the inverter, batteries, or other parts of the system. It’s important to work with a qualified professional to ensure any upgrades or replacements are done correctly and safely.
Regular maintenance and upkeep of your solar panel system will ensure it continues to produce clean energy for many years to come, providing you with significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
Benefits of residential solar panel systems
Reduction in energy costs
One of the most significant benefits of installing a residential solar panel system is the reduction in energy costs. By generating your own electricity, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your monthly electricity bill, saving you money over the long term.
Increase in home value
A residential solar panel system can also increase the value of your home. According to a study by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, homes with solar panels sold for an average of $15,000 more than homes without them.
Environmental benefits
By generating your own electricity from solar energy, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner environment. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution.
Overall, installing a residential solar panel system can provide numerous benefits, including cost savings, increased home value, and environmental sustainability. With advances in technology and government incentives, there has never been a better time to consider going solar.
Potential drawbacks and Considerations of residential solar panel systems
Upfront cost
One of the biggest potential drawbacks of residential solar panel systems is the upfront cost. While the long-term savings can be significant, the initial investment can be a barrier for some homeowners.
Potential limitations based on home and roof type
The type of home and roof can also impact the feasibility and effectiveness of a residential solar panel system. Factors such as roof orientation, shading, and age of the roof can all affect the performance of the system.
Weather and climate considerations
The weather and climate of the location of the home can also impact the effectiveness of a residential solar panel system. Areas with less sunlight or more frequent cloudy days may not be as suitable for solar energy generation.
Battery storage limitations
While battery storage can provide additional benefits such as backup power during outages, it can also add significant cost to a residential solar panel system. Additionally, the capacity and lifespan of batteries can also be a limitation.
It is important for homeowners to carefully consider these potential drawbacks and limitations when deciding whether to install a residential solar panel system. Working with a reputable and experienced installer can help address these considerations and ensure a successful installation.
Conclusion
Residential solar panel systems are an increasingly important tool for reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. In addition to their environmental benefits, solar panel systems can save homeowners money on their energy bills and increase the value of their homes. By generating their own electricity, homeowners can become more self-sufficient and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
If you’re a homeowner, now is the time to consider installing a solar panel system on your property. With government incentives and financing options available, there has never been a better time to invest in renewable energy. By making the switch to solar, you can take control of your energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future for all.
Looking ahead, the future of residential solar panel systems is bright. As technology continues to improve and become more affordable, we can expect to see more and more households adopt solar energy as a primary source of power. With the potential to reduce carbon emissions and save homeowners money, residential solar panel systems are a win-win for the environment and the economy.